BLOGS
What is Microbiome and Its Effect on Human Health
The word “microbiome” is a combination of the words “micro” and “biome,” referring to a “characteristic microbial community” of viruses, fungi, bacteria, and other microbes that colonize a particular space or ecosystem.
The microbiome consists of microorganisms interacting that can be both beneficial and harmful. Most are symbiotic (beneficial to the human body and the microbiota), and some are pathogenic microorganisms (harmful and promoting diseases). Different microorganisms depend on each other and live together in a healthy body. They adapt to and benefit from the conditions of the host.
Why is the gut microbiome so important?
Our bodies have several distinct microbiomes consisting of trillions of microorganisms—on the skin, in the mouth, and in our airways—but the most consequential one for health is in the gastrointestinal tract, commonly called the gut microbiome.
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem that consists of trillions of microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa—that live on or in our bodies. It’s composed of at least 100 trillion bacteria, which collectively weigh about three pounds (1.4 kilograms).
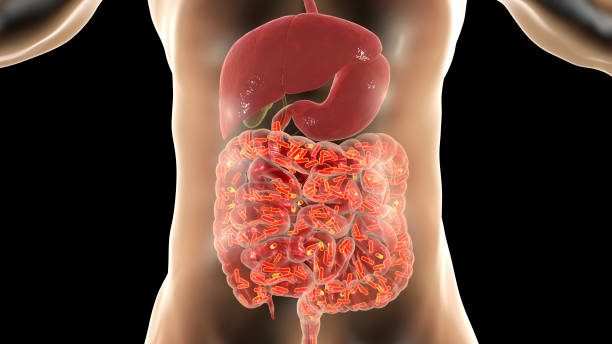
The human gut microbiome harbors trillions of microbial cells, which constitute more genomes than all the human cells in the body. The intestinal microbes constantly exchange chemical signals with the body’s cells and aid in the digestion of nutrients. These bacterial species form a symbiotic interaction with the body and contribute to the normal physiology of the gastrointestinal tract and other bodily organs and systems.
The human gut microbiota consists of diverse microbial communities in a complex microbial ecosystem depending on environmental factors. These environmental factors, such as pH, bile acid concentration, and peristalsis, regulate and segregate ecosystems from one another.
Advances in human microbiome research have helped further the understanding of the taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of microbial genomes and the multitude of factors that impact their microbial composition. This technology has opened many areas of research focused on the role of intestinal microbiota in immune system homeostasis that impacts human health and disease.
Suggested Read: Top Nutrients To Boost Your Immunity
What is the effect of the microbiome?
The activity and abundance of gut microbiomes rely on our unused metabolic products for their metabolism and, in turn, provide numerous benefits essential for optimal human health.

Metabolism
The essential metabolic mechanisms for the digestion of non-digestible substrates, such as food fibers and endogenous intestinal mucus, are provided by microbial metabolites. The fermentation of these food fibers causes the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) that can be utilized by the body as a nutrient source but also play a significant role in muscle function and the prevention of chronic diseases, such as irritable bowel syndrome. As a result, the host receives energy and substrates that can be absorbed, while the bacteria may grow and reproduce with access to the host’s energy and nutrients.
Immune System
A healthy person’s microbiome will also offer a defense against pathogenic bacteria that enter the body from sources like drinking or eating contaminated water or food. Prevotella, Ruminococcus, Bacteroides, and Firmicutes are a few of the large families of bacteria found in the human gut microbiota. These intestinal microbes prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria by competing for nutrition and adhering to the gut’s mucus membranes, a key location for immune action.
Suggested Read: Why Are Brands Going Paraben-Free
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a communication mechanism between the gut and the brain that combines neuronal, hormonal, and immune signaling. The brain requires a variety of neurochemicals produced by the gut microbiome to regulate physical and mental processes, such as memory, learning, and mood.
How does the environment affect the microbiome?
Our environment shapes our microbiome throughout life. A biodiverse environment that is microbe-rich may promote the development of healthy gut microbiota, increasing the gut bacterial species pool and lowering disease risk.
According to Mosca et al (2016), growing up in microbe-rich environments, like traditional farms, result in healthier children. The prevalence of inflammatory disorders is higher in modern cities because of reduced exposure to beneficial microbes from the environment, such as microbes from house dust or zoonotic microbes from animals.
The microbial composition of our human gut is predominantly influenced by the place of residence, lifestyle, environmental exposures, and living conditions. These environmental factors can influence and alter the composition of gut microbiomes and can lead to lower bacterial diversity, decreased SCFA production, and increased gut permeability. This can result in various disorders affecting energy metabolism, nutrient absorption, or immune system function.
In addition to microbial diversity of the immediate environment (home, air, soil, water, etc.), consideration should also be given to the biodiversity of the environment by documenting the details about the landscape and architecture, including the predominant vegetation structure and land use type, abiotic factors like climatic factors, and biodiversity of resident communities (i.e., plants, animals, etc.).
Improve Your Health With Crosswinds Tagaytay
Maintaining a good health is one of the most important things in a person’s life. Which is why it’s essential that you find a safe place wherein you nurture and improve your health while being surrounded by nature itself.
Given its proximity to Metro Manila, Tagaytay is an excellent choice for those seeking to escape to a rural environment with stunning natural surroundings along the natural slopes of the exclusive community without having to forego the modern conveniences they are accustomed to. Tagaytay’s outstanding environmental diversity and adequate microbial exposure are perfect for developing your gut microbiota.
Aside from that, you’ll have a front-row view of the city’s breathtaking scenery. Be one with nature as you experience a stunning sunrise in the morning and a sunset that will leave you in awe of its beauty. Explore the sight and scent of over 35,000 pine trees and the picturesque view of lush terrains beyond the corners of Tagaytay’s most beautiful luxury estate. Click here and indulge in one of the best and most renowned home builders in the Philippines.

Visit Brittany Corporation to learn more about several luxury residential communities, including La Posada in Sucat, Crosswinds Tagaytay, Portofino in Alabang, Promenade, and Georgia Club in Santa Rosa, Laguna, that are situated in some of the country’s most desirable locales. Here are some of the properties they have available.
You can also find them on social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube for the most recent news and updates, and answers to FAQs. You may also email them and make an appointment with them today.
Human Microbiome Project
The human microbiome research is mapping the human microbiome, revealing previously unknown species and closely related genome sequences. Its goal is to study the human as a supraorganism made up of non-human and human cells to describe the human microbiome and analyze its role in human diseases.
A person’s microbiome may influence their susceptibility to infectious diseases and contribute to chronic gastrointestinal diseases such as Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Some microbial communities influence how a person reacts to drug treatment. The mother’s microbiome may have an impact on her children’s health.
Genetic studies that measure the relative abundance of different species in the human microbiome have linked various combinations of unsocial organisms causing diseases in affected human populations.
A better understanding of the microbial diversity in the human microbiome could lead to new therapies, such as growing more good bacteria to treat infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria. The HMP is a road map for learning about the role of the microbiome in health, nutrition, immunity, and disease.
Final Words
Human gut microbiota evolves and appears to play an important role in both health and disease. An imbalance of harmful and beneficial microbes in the human gut may contribute to serious pathologic conditions.
Understanding how the external environment contributes to disease incidence and mortality requires considering several environmental factors in addition to our growing understanding of the microbiome.
Suggested Read: Benefits Of Tree Planting: Social And Environmental
Suggested Read: The Beauty Of Living In Brittany Santa Rosa
Suggested Read: Self-Care Month: A Vital Foundation In Life